spring 的IOC的依赖注入(DI)-------普通属性,集合的注入
本文共 2663 字,大约阅读时间需要 8 分钟。
一.普通属性注入
配置文件:
-->
实现类:
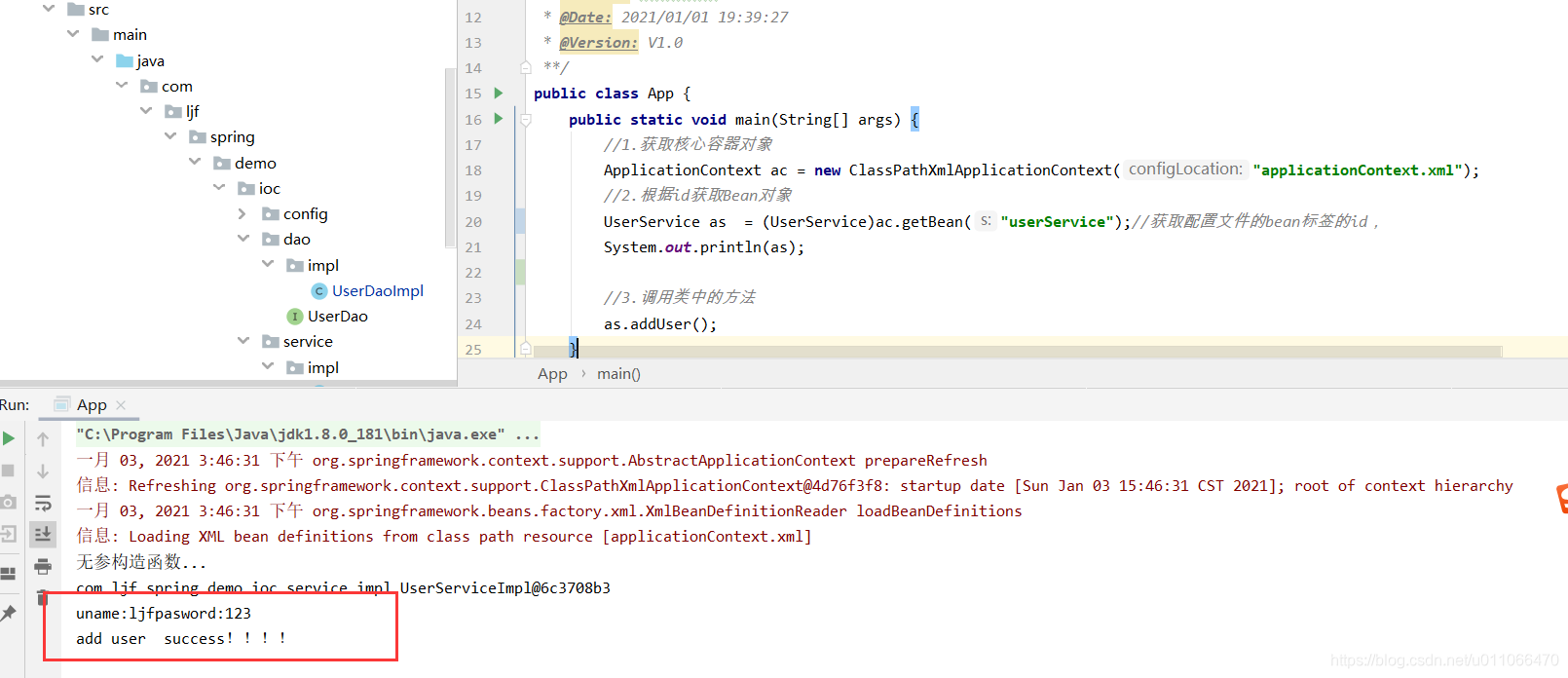
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private String userName; private String password; public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } private UserDao ud; //有参数构造函数 public UserServiceImpl(UserDao ud) { this.ud = ud; } //无参构造函数 public UserServiceImpl() { } /** public void setUd(UserDao ud) { this.ud = ud; } **/ public int addUser() { System.out.println("uname:"+userName+"pasword:"+password); return ud.addUser(); } 调用类:
二.集合的注入
1.配置文件
liu jian fu
2.service层
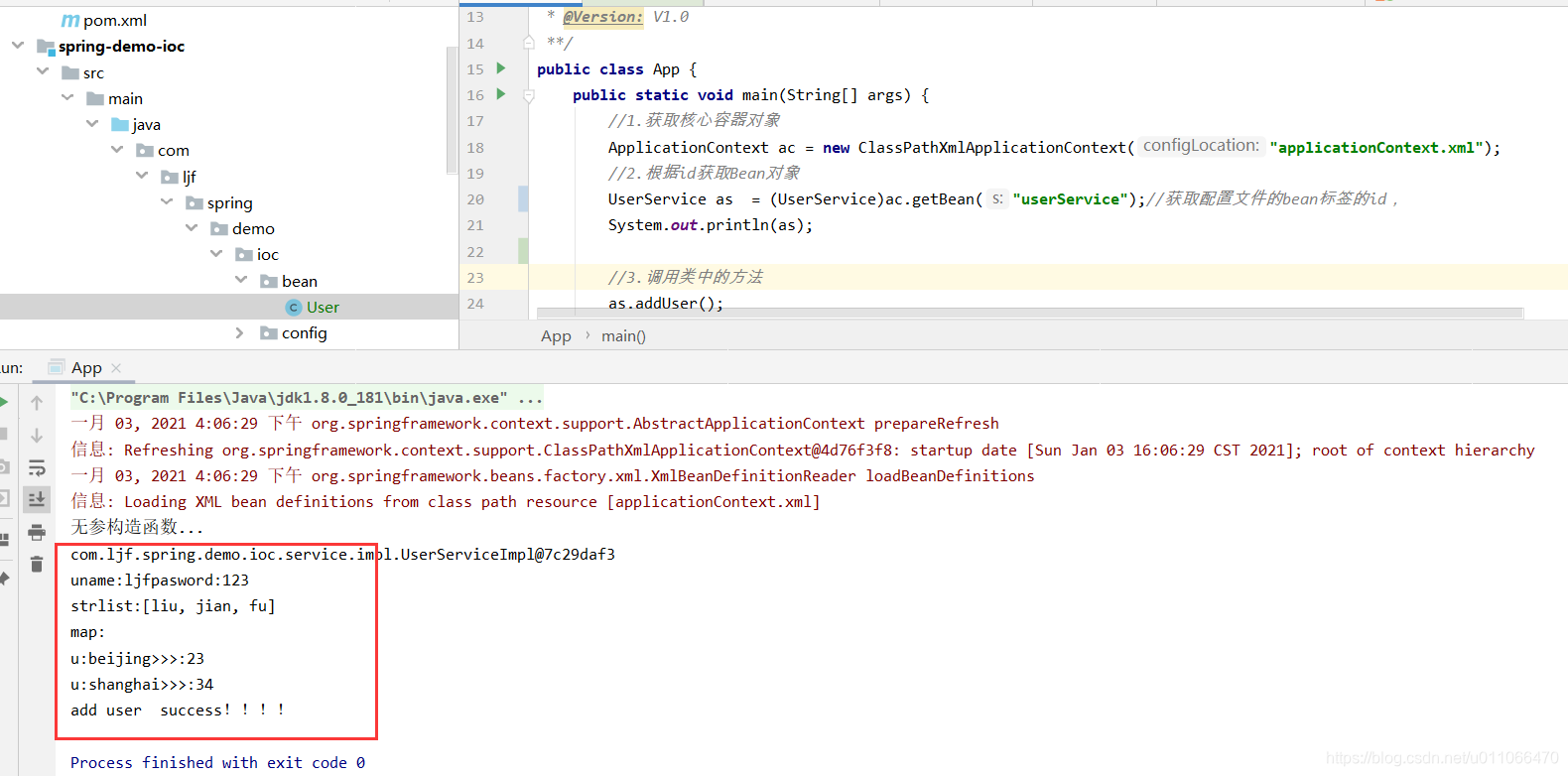
package com.ljf.spring.demo.ioc.service.impl;import com.ljf.spring.demo.ioc.bean.User;import com.ljf.spring.demo.ioc.dao.UserDao;import com.ljf.spring.demo.ioc.service.UserService;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;/** * @ClassName: UserServiceImpl * @Description: TODO * @Author: liujianfu * @Date: 2021/01/03 11:19:57 * @Version: V1.0 **/public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private List strNameList; private Map userMap; public List getStrNameList() { return strNameList; } public void setStrNameList(List strNameList) { this.strNameList = strNameList; } public Map getUserMap() { return userMap; } public void setUserMap(Map userMap) { this.userMap = userMap; } private String userName; private String password; public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } private UserDao ud; //有参数构造函数 public UserServiceImpl(UserDao ud) { this.ud = ud; } //无参构造函数 public UserServiceImpl() { } /** public void setUd(UserDao ud) { this.ud = ud; } **/ public int addUser() { System.out.println("uname:"+userName+"pasword:"+password); System.out.println("strlist:"+strNameList.toString()); System.out.println("map:"); for(String key:userMap.keySet()){ System.out.println("u:"+userMap.get(key).getName()+">>>:"+userMap.get(key).getAge()); } return ud.addUser(); }} 3.调用:
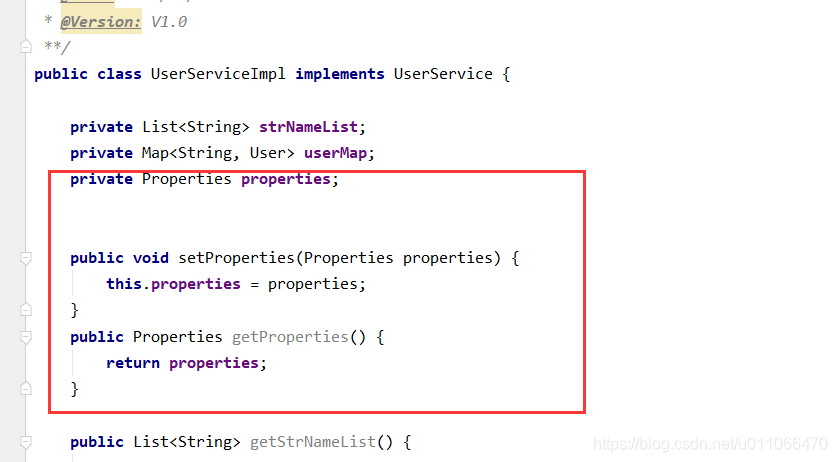
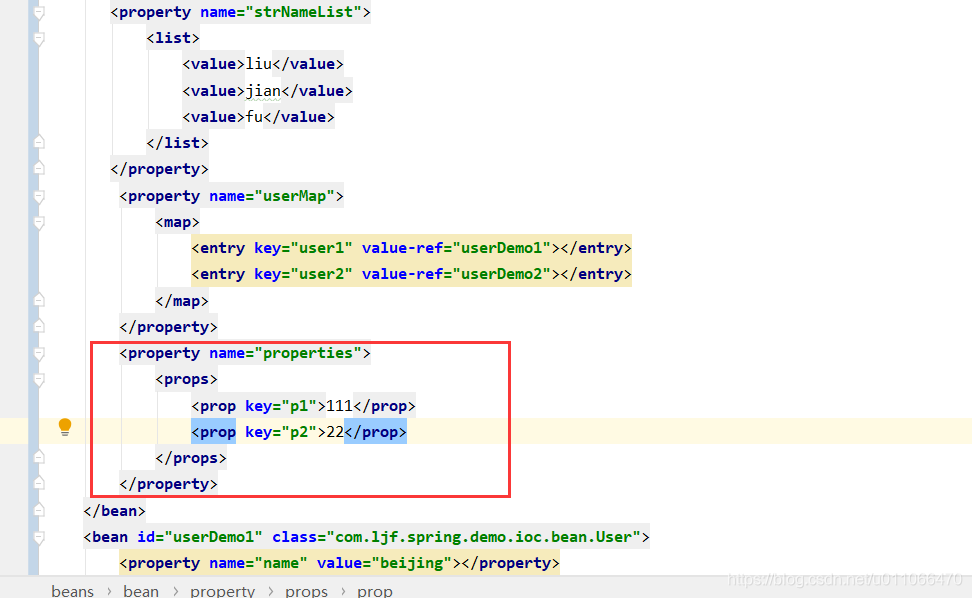
三.引用数据类型注入
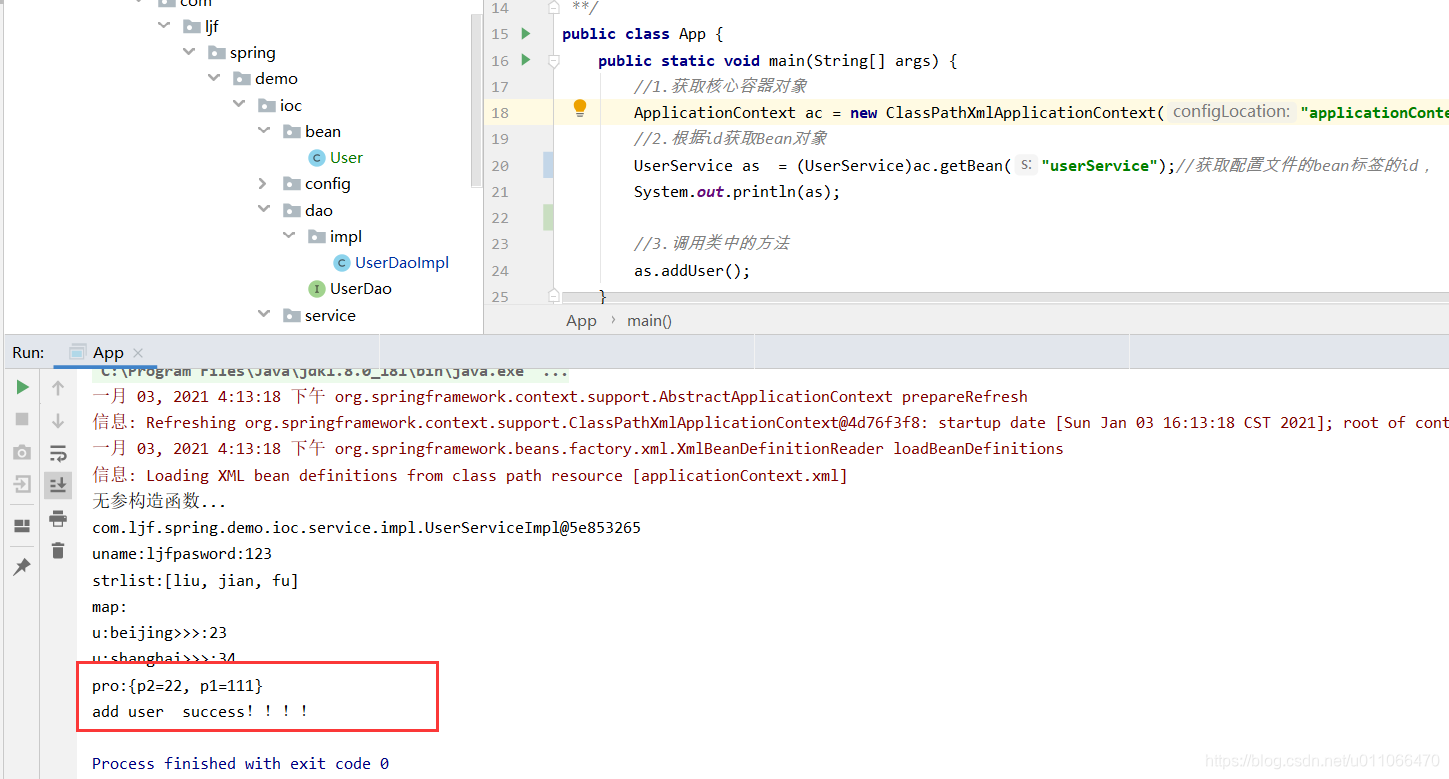
转载地址:http://beuzz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
Metasploit Web服务器渗透测试实战
查看>>
MFC模态对话框和非模态对话框
查看>>
Moment.js常见用法总结
查看>>
MongoDB出现Error parsing command line: unrecognised option ‘--fork‘ 的解决方法
查看>>
mxGraph改变图形大小重置overlay位置
查看>>
MongoDB可视化客户端管理工具之NoSQLbooster4mongo
查看>>
Mongodb学习总结(1)——常用NoSql数据库比较
查看>>
MongoDB学习笔记(8)--索引及优化索引
查看>>
mongodb定时备份数据库
查看>>
mppt算法详解-ChatGPT4o作答
查看>>
mpvue的使用(一)必要的开发环境
查看>>
MQ 重复消费如何解决?
查看>>
mqtt broker服务端
查看>>
MQTT 保留消息
查看>>
MQTT 持久会话与 Clean Session 详解
查看>>
MQTT工作笔记0007---剩余长度
查看>>
MQTT工作笔记0009---订阅主题和订阅确认
查看>>
Mqtt搭建代理服务器进行通信-浅析
查看>>
MS Edge浏览器“STATUS_INVALID_IMAGE_HASH“兼容性问题
查看>>
ms sql server 2008 sp2更新异常
查看>>